TURBT (Transurethral resection / scraping of Bladder Tumor) in NYC – Bladder Cancer Expert
What is TURBT (transurethral resection of bladder tumor)?
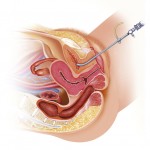
Transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure performed using the video-resectoscope. Video-resectoscope combines camera and a small telescope to visualize the inside of the urinary bladder. The resectoscope is introduced through the urethra into the bladder and the urological surgeon examines the urethra and the bladder visually for any lesions, masses and tumors or other abnormalities. If the surgeon notes a mass, tumor or suspicious lesion or any other abnormality he can take a biopsy or remove (resect or scrapes off) the tumor off the bladder wall. The area of resection is then cauterized to control bleeding. The catheter may be inserted by your urologist at the end of the procedure. Depending on the extent of the procedure the catheter may be kept for a few days to want to 2 weeks to allow bladder healing to occur.
[/col]
[col type=”three-fourth last”]TURBTs performed in the operating room under general spinal anesthesia. Postoperatively patients may experience frequent urination, urgency and some burning which improve over a period of a few weeks. A small amount of bleeding may also be noted in urine.
[/col]
Dr. Alex Shteynshlyuger, a fellowship trained urologic oncologist and a specialist in treating bladder cancer has performed hundreds of TURBT procedures.
Retrograde pyelograms during the TURBT.
A certain circumstances the urologist may determine that at retrograde pyelogram may be useful during TURBT. This may be done in patients who have not had preoperative upper tract imaging of the ureters and kidneys or who cannot have intravenous dye or who are found to have tumor close to the ureteral orifices.
Occasionally the tumor is close to the ureteral orifice the urologist may elect to place a ureteral stent to allow good healing of the tissue the stent may be kept anywhere from one to 6 weeks.
Mitomycin-C administration after TURBT
Administration of mitomycin-C after resection of bladder tumor has been shown to decrease the rates of tumor recurrence. Dr. Alex Shteynshlyuger routinely administers mitomycin-C to patients who have an medical indication (who are believed to benefit from it) for its use at the end of the procedure.
Many patients diagnosed with non-invasive bladder cancer may also benefit from BCG.